News | June 6, 2018
Warm Water Creeps into Otherwise-Calm Central Pacific
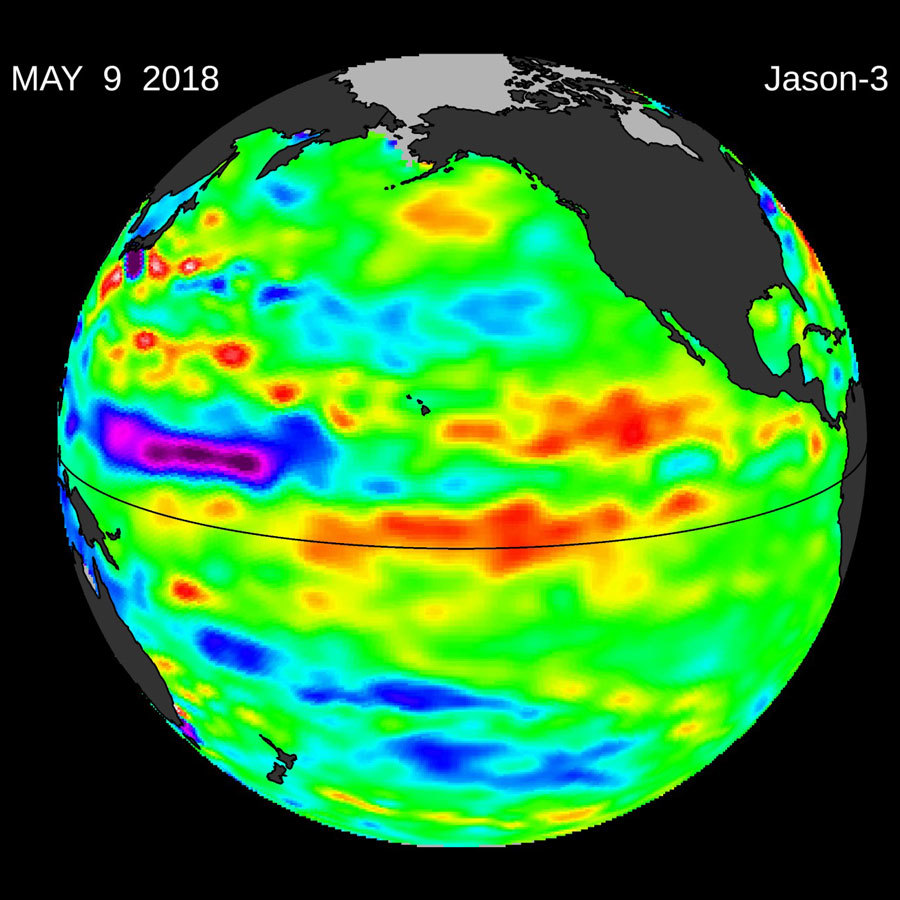
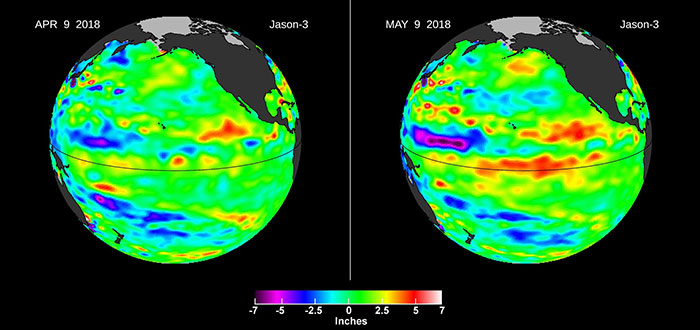
After a mild La Niña late last year, temperatures, convection and rainfall rates in the equatorial Pacific Ocean returned to normal by early April of this year. An April 9 image of sea level height from the U.S./European Jason-3 satellite mission showed most of the ocean at neutral heights. But by the beginning of May, high sea levels began to build up in the Central Pacific. In the tropics, high sea levels are usually caused by a layer of warm water at or below the surface.
This patch of high sea level is slowly traveling eastward through the tropical Pacific Ocean along the equator. Known as a downwelling Kelvin wave, this type of signal is often a precursor to an El Niño event.
The Kelvin wave formed after a few short periods when winds changed from the prevailing easterlies to westerly -- known as westerly wind bursts -- in the far western Pacific in early 2018. In addition, there has been a general weakening of the easterly winds along the equator since January. Both of these wind conditions combine to create the Kelvin wave, which moves east along the equator and results in the spreading of warm water layers that are normally confined to the western Pacific Ocean eastward into the central Pacific. The red pattern visible at the equator on May 9 is the result of this downwelling Kelvin wave.
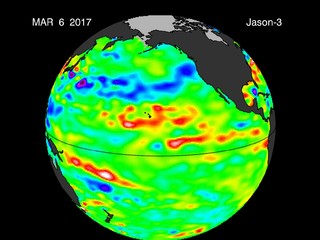
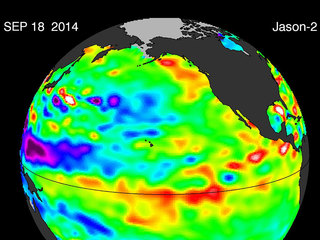
During a large El Niño, like the 2015-16 event, a huge area where sea levels are more than a foot (30 centimeters) higher than normal is visible in Jason-3 images. The high sea level is caused by a thick layer of warm water in the upper several hundred feet of the ocean. Such large El Niño events affect weather and climate across the globe, particularly in the western United States. In California, El Niños usually mean above-average winter rainfall, while Oregon and Washington typically see drier-than-normal winters.
El Niños happen when a series of Kelvin waves like this one spread warm water from west to east along the equator, causing high sea levels in the Central Pacific and sometimes as far east as the coastlines of Central and South America. The warm water is currently confined to the subsurface, with no warming at the ocean surface -- a first indicator of an upcoming El Niño event. But forecasters at agencies like the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) will be watching closely for more Kelvin waves like this one as summer approaches.
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, manages the Jason-3 mission for NASA. NOAA operates Jason-3 in partnership with NASA, the French space agency (CNES), and the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT).
News Media Contact Alan Buis Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California 818-354-0474 Alan.Buis@jpl.nasa.gov
Written by Carol Rasmussen NASA's Earth Science News Team